Introduction
In a world where products need to be tough, light, and eye-catching, hard anodized aluminum has stepped into the spotlight. This isn’t just a fancy term for engineers to toss around—it’s a material that’s rewriting the rules of design and durability. From the precision of CNC-machined airplane parts to the sleek shell of your smartphone, hard anodized aluminum is everywhere, quietly making things better. So, how does it work, and why should you care? Let’s dive in with a mix of science, real-world stories, and a peek at what’s next—because this stuff is too cool to ignore.
What is Hard Anodized Aluminum?
First things first: hard anodized aluminum starts as regular aluminum, but it gets a serious upgrade through an electrochemical process called hard anodizing. Unlike standard anodizing, which adds a thin, decorative layer, hard anodizing builds a thick, battle-ready coat of aluminum oxide—typically 25 to 100 microns deep. Picture aluminum getting a high-tech spa treatment in a sulfuric acid bath, zapped with cold, high-voltage currents to toughen it up.
Here’s where CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining comes in. Before anodizing, aluminum parts are often shaped with CNC machines—think precision milling or turning to carve out complex designs. The accuracy of CNC ensures the aluminum is perfectly prepped, with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances, so the hard anodized layer bonds evenly. The result? A lightweight material (about one-third the weight of steel) with a shield that’s insanely durable and corrosion-resistant. It’s no wonder industries are buzzing about hard anodized aluminum benefits.
The Science Behind Hard Anodized Aluminum
So, what’s the magic trick? During hard anodizing, aluminum sits in an acid bath while electricity sparks a reaction, growing a dense oxide layer right into the metal’s surface. This isn’t a flimsy coating—it’s part of the aluminum itself, so it won’t peel off. Compared to regular anodizing’s 5-25 microns, hard anodizing delivers 25-100 microns of protection, with a hardness of HV 400-600—tougher than some ceramics.
CNC machining plays a big role here too. Because the oxide layer adds a bit of thickness (about 50% grows outward), designers use CNC to craft parts with exact dimensions, leaving room for that extra layer. A poorly machined surface—say, with burrs or uneven spots—could mess up the anodizing, leading to weak spots. With CNC’s precision, manufacturers get a flawless base for a flawless finish. It’s a science that’s as practical as it is impressive.
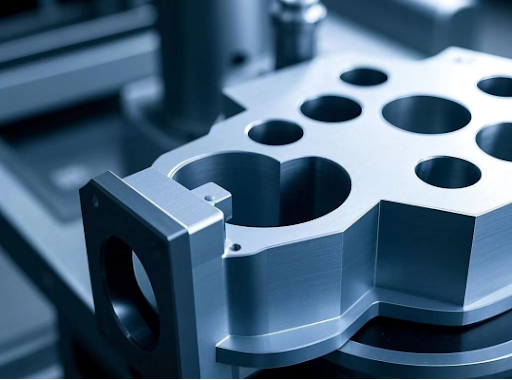
Three Key Benefits of Hard Anodized Aluminum
Why is hard anodized aluminum taking over? Here’s the rundown:
- Unmatched Durability and Wear Resistance
With a hardness of HV 400-600, this stuff shrugs off scratches and wear that would trash regular aluminum (HV 20-50). CNC-machined gears or hinges made from it can handle relentless use—like thousands of cycles in a factory or daily flips of a laptop lid. - Top-Notch Corrosion Resistance
That thick oxide layer blocks moisture, chemicals, and salt like a champ. For CNC-crafted car parts exposed to road grime, it’s a lifesaver, keeping rust at bay for years. - Lightweight Powerhouse
At one-third the weight of steel, it’s a dream for weight-sensitive designs. CNC machining shapes it into intricate, lightweight components—like aircraft brackets—without sacrificing strength.
Table 1: Hard Anodized Aluminum vs. Regular Aluminum
| Property | Hard Anodized Aluminum | Regular Aluminum |
| Hardness (HV) | 400-600 | 20-50 |
| Oxide Layer Thickness (μm) | 25-100 | 5-25 |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior | Moderate |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
This table shows why hard anodizing turns aluminum into a superstar—perfect for CNC precision and real-world toughness.
Cross-Industry Applications of Hard Anodized Aluminum
Hard anodized aluminum is a jack-of-all-trades, shining in industries where CNC machining meets high stakes:
- Aerospace: Sky-High Precision
In aerospace, CNC machines carve aluminum into landing gear or wing supports, then hard anodizing adds durability. The combo cuts weight (crucial for fuel savings) and fights corrosion from high-altitude moisture. - Automotive: Revving Up Efficiency
Car makers use CNC to shape pistons or chassis parts, followed by hard anodizing for wear resistance and a sleek look. It’s lighter than steel, tougher than untreated aluminum, and rust-proof—ideal for modern vehicles. - Consumer Electronics: Everyday Heroes
Your phone or laptop case? Probably CNC-milled aluminum, hard anodized for scratch resistance and style. Companies like Apple love it for its lightweight strength and dye-friendly surface.
CNC machining is the unsung hero here. Its ability to churn out complex, repeatable parts pairs perfectly with hard anodizing’s protective punch. Together, they deliver products that perform and last.
Table 2: Hard Anodized Aluminum Applications Across Industries
| Industry | Component | Key Benefits |
| Aerospace | Landing Gear, Panels | Lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant |
| Automotive | Pistons, Body Panels | Weight reduction, wear resistance, sleek finish |
| Electronics | Phone Cases, Laptops | Scratch-proof, stylish, lightweight |
This table proves hard anodized aluminum applications are a CNC-driven win across the board.

Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
Here’s a twist: hard anodized aluminum isn’t just tough—it’s eco-friendly too. The anodizing process uses fewer harsh chemicals than traditional coatings, and waste like spent electrolytes can often be recycled. Pair that with CNC’s efficiency—minimizing material waste through precise cuts—and you’ve got a green combo.
Plus, durability means longevity. A CNC-machined, hard anodized part lasts longer, reducing replacements and landfill clutter. For companies chasing sustainability goals, this is a material that delivers without compromise.
Table 3: Environmental Impact of Hard Anodizing
| Factor | Hard Anodizing | Traditional Coatings |
| Hazardous Chemicals | Low | High |
| Waste Recyclability | High | Low |
| Energy Use | Moderate | High |
| Product Longevity | Extended | Standard |
| Carbon Footprint | Reduced | Higher |
This table underscores hard anodizing’s edge—less waste, more life, all thanks to smart processes like CNC.
Innovations and Future Trends in Hard Anodized Aluminum
The future’s bright for hard anodized aluminum. Researchers are tinkering with anodizing recipes to boost hardness or add wild colors—think tougher CNC-machined prosthetics or vibrant solar panel frames. CNC technology is evolving too, with faster, smarter machines that can handle trickier designs, making hard anodizing even more versatile.
For designers, new dyeing tricks mean bolder aesthetics—imagine a CNC-crafted smartwatch that’s both rugged and radiant. As CNC and anodizing tech advance together, expect hard anodized aluminum applications to pop up in unexpected places.
Boosting Product Durability with Hard Anodized Aluminum
At its heart, hard anodized aluminum is about longevity. Its wear resistance keeps CNC-machined surfaces pristine, its corrosion protection battles the elements, and its lightweight strength ensures top performance. In critical uses—like a jet turbine or a medical tool—this reliability is non-negotiable. Even in daily gear, like a CNC-shaped bike frame, it’s a game-changer. Durability isn’t just practical—it’s a promise of quality that sells.
Hard anodized aluminum, paired with the precision of CNC machining, is more than a material—it’s a revolution. It’s turning out tougher, lighter, smarter products across industries, from aerospace to your pocket. With its blend of durability, style, and sustainability, it’s a designer’s dream and an engineer’s best friend. As CNC tech and anodizing innovations keep rolling, hard anodized aluminum will stay ahead of the curve—building a future that’s built to last.
And if you’re curious to dig deeper, parts of this piece drew inspiration from an insightful article by the folks at why-choose-hard-anodized-aluminum-for-cnc-machined-parts—click here to explore more on how hard anodized aluminum analysis are reshaping manufacturing.
FAQ:
- What is hard anodized aluminum, and how is it different from regular aluminum?
Hard anodized aluminum is aluminum that’s undergone a special electrochemical process to create a thick, durable oxide layer on its surface—typically 25-100 microns thick, compared to regular aluminum’s untreated state or the thinner 5-25 microns from standard anodizing. This process, often paired with CNC machining for precision shaping, boosts hardness (HV 400-600 vs. HV 20-50 for regular aluminum), wear resistance, and corrosion protection while keeping it lightweight. Think of it as aluminum with a superhero upgrade—tougher and ready for action.
- How does hard anodized aluminum work with CNC machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining and hard anodized aluminum are a dream team. CNC machines—using precise milling, turning, or cutting—shape aluminum into intricate parts with tight tolerances. After that, hard anodizing adds a protective oxide layer. The precision of CNC ensures the surface is smooth and uniform, which is critical because any flaws (like burrs) could weaken the anodized finish. Together, they deliver parts that are both perfectly formed and incredibly durable, from aerospace components to phone casings.
- What are the main benefits of using hard anodized aluminum in products?
Hard anodized aluminum shines with three big perks: durability, corrosion resistance, and lightweight strength. Its hardness (HV 400-600) makes it resist scratches and wear—like a CNC-machined gear surviving thousands of cycles. The thick oxide layer fights off rust and chemicals, perfect for car parts or outdoor gear. And at one-third the weight of steel, it’s a go-to for designs needing strength without bulk, like aircraft parts. Plus, it looks sleek and can be dyed, adding style to function.
- Which industries use hard anodized aluminum the most?
You’ll find hard anodized aluminum everywhere! Aerospace relies on it for lightweight, corrosion-resistant parts like landing gear, often CNC-machined for precision. Automotive uses it in pistons and body panels to cut weight and boost durability. Consumer electronics—like phones and laptops—love its scratch-proof, stylish finish. It’s also big in medical devices (think surgical tools) and even cookware, where durability meets everyday use. Its versatility makes it a cross-industry favorite.
- Is hard anodized aluminum environmentally friendly?
Yes, it’s greener than you might think! Compared to traditional coatings, hard anodizing uses fewer harsh chemicals, and its waste—like electrolyte solutions—can often be recycled. CNC machining adds to this by reducing material waste with precise cuts. Best of all, products made with hard anodized aluminum last longer due to their wear and corrosion resistance, meaning fewer replacements and less landfill junk. It’s a solid pick for eco-conscious manufacturers.
- Can hard anodized aluminum be customized for design purposes?
Absolutely! One of its coolest tricks is flexibility in design. After CNC machining shapes the aluminum, hard anodizing can be tweaked—think thicker layers for extra toughness or smoother finishes for looks. It can also be dyed in various colors, from subtle blacks to bold reds, making it a hit for consumer products like smartwatches or laptop casings. This blend of strength and style lets designers get creative without compromising performance.
- What’s the future of hard anodized aluminum in product design?
The future looks exciting! Researchers are pushing hard anodized aluminum to new heights—testing ways to make it harder or more colorful. Paired with advances in CNC machining (faster, smarter machines), it could mean tougher prosthetics, longer-lasting solar panels, or even flashier gadgets. As sustainability and lightweight design stay hot topics, expect hard anodized aluminum to keep popping up in innovative, game-changing products.
- How does hard anodized aluminum improve product durability?
Durability is its superpower. That hard oxide layer (HV 400-600) resists wear, keeping CNC-machined surfaces pristine through heavy use—like a bike frame or industrial tool. It also fights corrosion, so products don’t degrade in harsh conditions (think salty air or engine oil). And its lightweight strength means it performs without cracking under pressure. Whether it’s a jet engine or a kitchen pan, hard anodized aluminum makes things last longer—and that’s a win for everyone.
