Excerpt: RTO in cybersecurity goes hand in hand with RPO which decides how much time a business will take to get back to normalcy after a cyberattack.
Key Phrase: What is RTO in cybersecurity
When Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) said, “Time is money,” no one thought it would become a critical parameter in business data recovery models and security risk management systems. Today, businesses spend a huge amount of money on data privacy in the event of data theft for disaster management and lawsuits.
Business models and time as key determining criteria
(Photo: CloudWave)
Business models that focus on growth place a timeline under each end goal. This time limit sets key areas of work which get assigned to the respective staff who fulfill the goal. However, this model lacked a flexible disaster recovery plan which hackers across the globe have exploited.
Moreover, hacking systems and releasing sensitive data on the dark web have become a catastrophe that is worked upon with models catering to data and time. While RTO is about time, RPO deals with data lost in a cyber event.
What is RTO in cybersecurity?

(Photo: Atomic Data)
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity planning that is implemented once cybercriminals render services completely inaccessible. Disasters like DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks can lead to system unavailability or crashes that last for minutes, hours, days, or even longer.
During such events, the unavailability of specific services can have severe consequences. For instance, healthcare systems being down could prevent patients from receiving diagnoses, while a targeted bank may prevent users from accessing their accounts.

An example of RTO set by a company (Photo: ResearchGate)
Such hindrances can lead to loss of customers, credibility, and delayed services for an unforeseen duration of time. To combat the uncertainty of time for when services will be back online, the recovery time objective step creates an estimated timeline around which the IT (Information Technology) staff needs to meet the deadline and bring the systems back.
Here, the nature of the business plays a crucial role in determining the urgency with which the systems need to be restored, whether it’s within weeks, days, or even hours. For example, if healthcare services are interrupted for weeks, it will pose a severe risk to life.
The role of RTO in cybersecurity and business recovery models
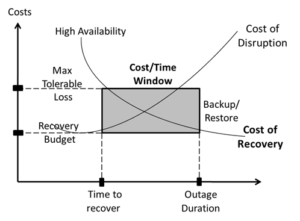
Instrumental factors including cost of recovery (Photo: BCM Institute)
A Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plan (BC-DR Plan) creates a recovery target for various scenarios that could impact operations and lead to consequences not just for the business holders but also for the consumers.
The decision regarding the Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plan is based on the potential damage that may occur if services are impeded. These damages are evaluated in terms of business loss, data loss, monetary loss, and the urgency of hindered services, among other factors.

Factors deciding the RTO (Photo: MSP 360)
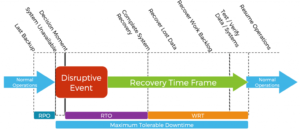
- Recovery Time Objective – The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is a metric that determines the time required for an organization to recover from an outage or a security incident. Businesses can thrive even in the face of security incidents by implementing backups and other risk-reducing measures. These strategies ensure that the organization can minimize both potential risks and losses.
- Recovery Point Objective – In case of a cyber attack, the recovery point objective (RPO) is the maximum amount of data loss that an organization can tolerate. This data can be segregated into sensitive, classified, and private categories, creating a severity ratio in case of data theft.
- Recovery Time Frame – The RTF is a combination of the RPO and the working recovery time after a cyber attack.
- Maximum Tolerable Downtime – After a cyber attack, the time an organization can still stretch its functions until normal business operations are resumed is the MTD.
Need for Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) in cybersecurity
Organizations may go for Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) software to find a solution to cyber-attacks which helps reduce the recovery time. If the RTO set for a company is an hour, they may go for redundant database backup on remote systems to reduce the time for recovery.
RTO in cybersecurity ensures that the recovery is not only data-focused but also cost-effective. It suggests the recovery process and the challenges that may be faced while pursuing the steps involved. Therefore, every organization must stay up-to-date on what RTO is in cybersecurity by finding solutions through research, experts, cybersecurity magazines, threat intelligence, and cybersecurity news.